What’s a Subdomain & How Is It Used?
Subdomains serve as an extension of your main domain, providing a method to organize and navigate different sections of your website efficiently. For instance, a subdomain like blog.example.com separates blog content from the main site, optimizing user navigation and potentially enhancing SEO. Speaking of SEO, understanding Domain Authority and its impact can further refine your strategy when deploying subdomains.
What Are Subdomains Used For
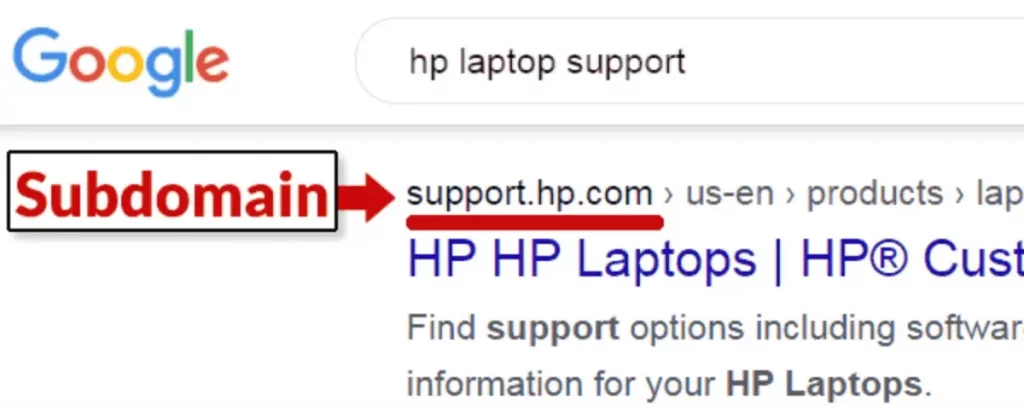
Subdomains are incredibly versatile, used for hosting blogs, online stores, or customer support sections separately from the main website. This separation aids in content organization and caters to different user experiences. For example, businesses can leverage subdomains for targeting specific keywords or regions, which aligns with strategies for boosting Topical Authority in SEO.
Subdomain Examples
- Blog.example.com: A dedicated space for a company’s articles, updates, and discussions.
- Shop.example.com: An online storefront, distinct from the company’s main informational website.
- Support.example.com: A customer support hub with FAQs, contact information, and forums.

What are the benefits of subdomains?
Subdomains offer several key advantages, including improved organization and enhanced SEO. They allow for increased scalability and customization, tailoring content to specific needs or audiences. For those interested in expanding their web presence, understanding the Ultimate Guide to Dropped Domains can provide insights into acquiring valuable, pre-existing subdomains.
- Improved Organization: They help in logically separating website sections, making it easier for users to find what they’re looking for.
- Enhanced SEO: Properly used subdomains can boost your SEO efforts by enabling you to target specific keywords and create niche content areas.
- Increased Scalability: Subdomains allow your site to expand flexibly, adding new sections without interfering with the main site’s structure or content.
- Customization: Each subdomain can have its own distinct design, navigation, and user experience, catering to the specific needs of its content or audience.
Understanding URL Structure
The URL structure is crucial in understanding how subdomains fit into the broader web architecture. By effectively utilizing subdomains, website owners can enhance user experience and improve SEO. Those looking to optimize their online presence might consider building a Lead Generation Website That Converts, where strategic use of subdomains can play a crucial role.
What Is the Difference Between a Subdomain and a Domain

The distinction between a domain and a subdomain is foundational to understanding web architecture. A domain, often referred to as a ‘root domain,’ is the central web address that you purchase to host your website, such as example.com. It’s the core of your website’s identity on the internet, representing your brand and hosting your content.
A subdomain, on the other hand, acts as a secondary website under the main domain, signifying a specific section or service, like blog.example.com. While a domain forms the basis of your web presence, subdomains allow for the organization and segmentation of your website into discrete areas with distinct content or functionalities.
Domain Name Checker
A domain name checker is an online tool that helps determine the availability of a desired domain name. By entering the name you wish to register, the checker can instantly tell you if it’s available for purchase or already taken. This tool is essential for businesses and individuals planning to establish a new website, ensuring they find a unique and suitable domain name that reflects their brand or purpose.

What Is the Difference Between a Subdomain and a Subdirectory
The difference between a subdomain and a subdirectory (also known as a subfolder) revolves around website structure and SEO considerations. A subdirectory is a folder within your main website, indicated in the URL after the domain name, such as example.com/blog. It’s part of the main domain and inherits its SEO authority.
Subdomains, as mentioned, function as separate entities from the main domain, potentially having their own distinct set of SEO metrics. This distinction influences how search engines index and rank website content.
When is a subdirectory better than a subdomain?
Subdirectories are preferable when you want to keep your site’s architecture simple and maintain the SEO authority concentrated within a single domain. They are ideal for content that is closely related to the main theme of your website, such as a blog or a product catalog, where you aim to leverage the domain’s existing authority and ensure a cohesive user experience.
When is a subdomain better than a subfolder?
Subdomains excel in scenarios where you need to distinctly separate different areas of your website that might not be directly related or when targeting different geographical regions or languages. They offer more flexibility in customization and can be treated by search engines as separate entities, which can be advantageous for specific SEO strategies. Additionally, subdomains can host entirely different platforms or technologies, making them suitable for hosting a web application or a forum that requires a unique server configuration separate from the main website.
3 Subdomain Examples
To illustrate the versatility and utility of subdomains, consider the following examples:
- Blog.example.com: A dedicated space for hosting a blog, allowing a company to publish articles, news, and updates without mixing content with the main website’s commercial or informational sections.
- Store.example.com: An e-commerce platform under the main domain, enabling businesses to separate their online storefront from other website content, thereby focusing on online sales.
- Support.example.com: A customer support portal offering FAQs, ticket submissions, and resource guides, providing users with a dedicated area for help and support.
These examples showcase how subdomains can serve distinct functions, improving site organization and user navigation.
How to Create a Subdomain

Creating a subdomain involves several straightforward steps:
- Access Your Hosting Control Panel: Log in to the control panel provided by your web hosting service.
- Navigate to the Domain Section: Look for the ‘Domains’ or ‘Subdomains’ section in your control panel.
- Create the Subdomain: Enter the desired subdomain prefix in the provided field and select the domain to which it will be attached. For example, entering ‘blog’ will create blog.example.com.
- Configure and Publish: Depending on your host, you may need to configure certain settings for your subdomain. Once configured, you can start uploading content to your new subdomain or install a platform like WordPress to manage it.
The process may vary slightly depending on your hosting provider, so consulting their specific documentation or support services is advisable for guidance.
Conclusion
Subdomains are a powerful feature that allows for the structured and efficient organization of various sections of a website under a single domain. By understanding and leveraging subdomains, website owners can enhance user experience, improve SEO performance, and tailor content to specific needs or audiences. Whether for hosting a blog, an online store, or a support hub, subdomains offer a flexible and effective solution for website management and growth.
What Are Subdomains FAQ
and stay up-to-date with the latest news about our platform and affiliate marketing.




